Paleontologists reaffirm the cause of dino extinction
Sunday, March 7, 2010
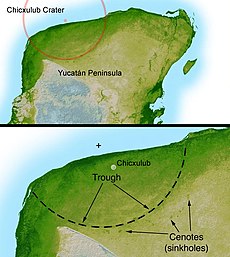
A group of 41 paleontologists and researchers reaffirmed the cause of dinosaur extinction. The research team concluded that a giant asteroid killed dinosaurs over 65 million years ago. The asteroid crashed into Yucatán, Mexico creating the Chicxulub crater. Their report was published Friday in the academic journal Science.
In 1980, Louis Alvarez and son, Walter, had published a paper stating that an asteroid had killed the dinosaurs. The Chicxulub crater was also discovered in Mexico at approximately that same time, therefore the theory gained scientific acceptance. More recent explanations of the cause of dinosaur's extinction included that perhaps volcanic eruptions on Deccan traps or multiple asteroid crashes ended the dinosaurs' existence.
The team performed chemical analyses of soil and fossil samples, where a high concentration of iridium (which is commonly found in asteroids and meteors) was found, which dated back to the approximate time of the asteroid crash.
The asteroid measured approximately 7.5 miles wide, and hit with an impact of one billion times the force of the Hiroshima atomic bomb. The impact would have immediately killed all animals and plant life within the radius of half of a continent. With such an impact, debris would have flown into the air and then fallen back into the atmosphere with the force of a ballistic missile.
The crash of this asteroid into the earth would have also caused the equivalent of the heat of ten noonday suns, which would have burned the skin or feathers of dinosaurs, and created wildfires on any plant life which had survived to that point. The crash would have also triggered massive earthquakes and tsunamis, possibly causing parts of continents to fall into the ocean.
The area of Yucatán which the asteroid struck had also been rich in sulfur, which was blasted out of the earth and into the sky, where it would have mixed with water vapors, creating clouds that rained sulfuric acid, and which would block out the sun for approximately a decade.
Sources
- Ethan Sacks. "Mystery solved! Giant asteroid killed the dinosaurs, say scientists" — NY Daily News, March 5, 2010
- Associated Press. "Experts reaffirm asteroid killed dinosaurs" — Associated Press, March 4, 2010
- Thomas H. Maugh II. "Scientists settle on single-asteroid hit as culprit in dinosaurs' demise" — Los Angeles Times, March 4, 2010